Introduzione alla Tecnologia dell'Osmosi Inversa
L'osmosi inversa (OI) è una tecnologia di separazione basata su membrana che utilizza la pressione come forza trainante per rimuovere solidi disciolti, ioni e altre impurità dall'acqua. Applicando una pressione superiore alla pressione osmotica dell'acqua di alimentazione, le molecole d'acqua vengono forzate attraverso una membrana semipermeabile, mentre i contaminanti vengono respinti e concentrati nel flusso di salamoia. Questo processo riduce efficacemente la salinità, la durezza, la materia organica e i microrganismi, producendo acqua permeata di elevata purezza.
I sistemi a osmosi inversa sono ampiamente utilizzati nella desalinizzazione dell'acqua di mare e salmastra, nel riutilizzo delle acque reflue industriali, nella purificazione dell'acqua potabile e in vari processi industriali che richiedono acqua di alta qualità. Le prestazioni e l'efficienza dell'OI dipendono da fattori quali il materiale della membrana, la qualità dell'acqua di alimentazione, la pressione di esercizio e la progettazione del sistema.
In condizioni di equilibrio, la differenza di altezza tra i due compartimenti corrisponde alla differenza di pressione osmotica (tipicamente indicata come π) della soluzione alla concentrazione di equilibrio. La pressione osmotica è una funzione del tipo e della concentrazione dei soluti nella soluzione. Generalmente, per ogni 100 ppm di concentrazione di solidi totali disciolti (TDS), la pressione osmotica π varia da 0,04 a 0,075 bar.
π = nRT = MM RT
V
n = la quantità di soluto in moli
R = la costante dei gas ideali
T = temperatura in Kelvin
V = il volume della soluzione
MM = la massa molare del soluto
Per esempio:
Una soluzione di acqua salmastra con un TDS di 1.500 ppm ha una pressione osmotica di circa 1,02 bar;
Una soluzione di acqua di mare con un TDS di 32.000 ppm ha una pressione osmotica di circa 21,8 bar.
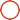
Osmosi | Equilibrio | Osmosi Inversa
Osmosi Naturale
Bassa Concentrazione di Soluto → Alta Concentrazione di Soluto
Membrana Semipermeabile
Pressione Esterna Applicata
L'osmosi inversa (OI) si riferisce al processo in cui l'acqua scorre nella direzione opposta all'osmosi naturale, da una soluzione concentrata a una diluita. Questo processo deve essere guidato dalla pressione applicata esternamente. Il flusso inverso dell'acqua è ostacolato da tre fattori principali: la pressione osmotica su entrambi i lati della membrana semipermeabile, la resistenza interna della membrana stessa e la resistenza causata dall'incrostazione sulla superficie della membrana e all'interno dei suoi pori durante il funzionamento. Pertanto, la pressione applicata nell'osmosi inversa deve superare significativamente la differenza di pressione osmotica della soluzione.
Per esempio:
-
Nei sistemi OI ad acqua salmastra, la pressione di esercizio è tipicamente impostata a 15,5 bar (o superiore), mentre la differenza di pressione osmotica di una soluzione di acqua salmastra a 2.000 ppm è inferiore a 2 bar.
-
Per l'acqua di mare con una differenza di pressione osmotica di circa 22 bar (a 32.000 ppm), la pressione di esercizio applicata è solitamente di circa 55 bar.
-
1.2 Membrane a Osmosi Inversa
Il sistema a osmosi inversa si basa su membrane a osmosi inversa (ovvero le membrane semipermeabili sopra menzionate) per ottenere la separazione tra solventi e soluti. Queste membrane consentono il passaggio di solventi respingendo altri soluti. Attualmente, la maggior parte delle membrane a osmosi inversa presenta una struttura polimerica composita multistrato con poliammide come strato di separazione. Queste membrane offrono eccellenti prestazioni di separazione e durata a lungo termine in condizioni convenzionali di acqua di alimentazione.
1.3 Parametri Chiave di Prestazione
1. Tasso di Recupero
Il tasso di recupero si riferisce alla percentuale di acqua di alimentazione che viene convertita in acqua permeata. Ad esempio, un tasso di recupero del 75% significa che per ogni 100 m³/d di acqua di alimentazione, l'uscita di acqua permeata è di 75 m³/d.
- Per un singolo elemento di membrana a osmosi inversa industriale, il tasso di recupero nei test di prestazione del prodotto varia tipicamente dall'8% al 15%. Per un sistema di trattamento dell'acqua a osmosi inversa su larga scala, il tasso di recupero varia tra il 40% e il 90%, a seconda di fattori quali le caratteristiche dell'acqua di alimentazione (ad esempio, concentrazione di sale, contaminanti), la configurazione del sistema e le condizioni operative.
- 2. Tasso di Reiezione
Il tasso di reiezione definisce la percentuale di un soluto specifico trattenuto dalla membrana a osmosi inversa dopo la filtrazione rispetto alla sua concentrazione nell'acqua di alimentazione.
-
-
Valenza dei Soluti: I soluti con valenza più alta mostrano tassi di reiezione più elevati. Ad esempio, Ca²⁺ ha un tasso di reiezione più elevato rispetto a Na⁺.
-
Grado di Idratazione: Gli ioni con dimensioni idratate maggiori raggiungono tassi di reiezione più elevati. Ad esempio, gli ioni cloruro (Cl⁻) vengono respinti in modo più efficace rispetto agli ioni nitrato (NO³⁻).
-
Peso Molecolare: Generalmente, i soluti con pesi molecolari più elevati vengono respinti in modo più efficiente rispetto a quelli con pesi molecolari inferiori.
-
Polarità dei Soluti: I soluti non polari mostrano tipicamente tassi di reiezione inferiori. Ad esempio, il benzene, nonostante il suo peso molecolare relativamente elevato, ha un tasso di reiezione di solo circa il 25% a causa della sua struttura non polare.
-
Stato dei Soluti: I soluti gassosi non vengono respinti dalle membrane a osmosi inversa. Ad esempio, il gas ammoniaca (NH₃) non viene respinto, mentre gli ioni ammonio (NH₄⁺) in soluzioni a basso pH possono essere efficacemente trattenuti.
-
Grado di Ramificazione: Le molecole altamente ramificate mostrano tassi di reiezione più elevati. Ad esempio, l'isopropanolo ha un tasso di reiezione più elevato rispetto all'n-propanolo.
-
Altri Fattori: Ulteriori influenze includono le condizioni dell'acqua di alimentazione (ad esempio, pH, forza ionica, durezza) e le proprietà della membrana (ad esempio, carica superficiale caratterizzata dal potenziale zeta, idrofilia e morfologia della superficie).
Le prestazioni di reiezione delle membrane a osmosi inversa pratiche, in particolare le membrane di nanofiltrazione, dipendono da una combinazione dei fattori sopra indicati piuttosto che da una singola variabile. Per dati più accurati, i manuali dei prodotti e i test di simulazione su scala di laboratorio forniscono solo informazioni di riferimento preliminari. Si consiglia agli utenti di condurre test pilota in condizioni reali sul campo per convalidare le prestazioni.

 Il tuo messaggio deve contenere da 20 a 3000 caratteri!
Il tuo messaggio deve contenere da 20 a 3000 caratteri! Si prega di controllare la tua email!
Si prega di controllare la tua email!  Il tuo messaggio deve contenere da 20 a 3000 caratteri!
Il tuo messaggio deve contenere da 20 a 3000 caratteri! Si prega di controllare la tua email!
Si prega di controllare la tua email! 

