Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor(MBBR) Biological Filler Bio Carrier For Domestic And Industrial Sewage Treatment-MH-Series
ARTICLE
Moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) is a type of wastewater treatment process that was first invented by Professor Hallvard Ødegaard at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology in the late 1980s.[1] The process takes place in an aeration tank with activated sludge and uses floating, recycled plastic carriers that a biofilm can grow on. The compact size and cheap wastewater treatment costs offer many advantages for the system. The main objective of using MBBR is water reuse and nutrient removal or recovery. In theory, wastewater will be no longer considered waste, it can be considered a resource.

OVERVIEW
Due to early issues with biofilm reactors, like hydraulic instability and uneven biofilm distribution, moving bed biofilm technology was developed.
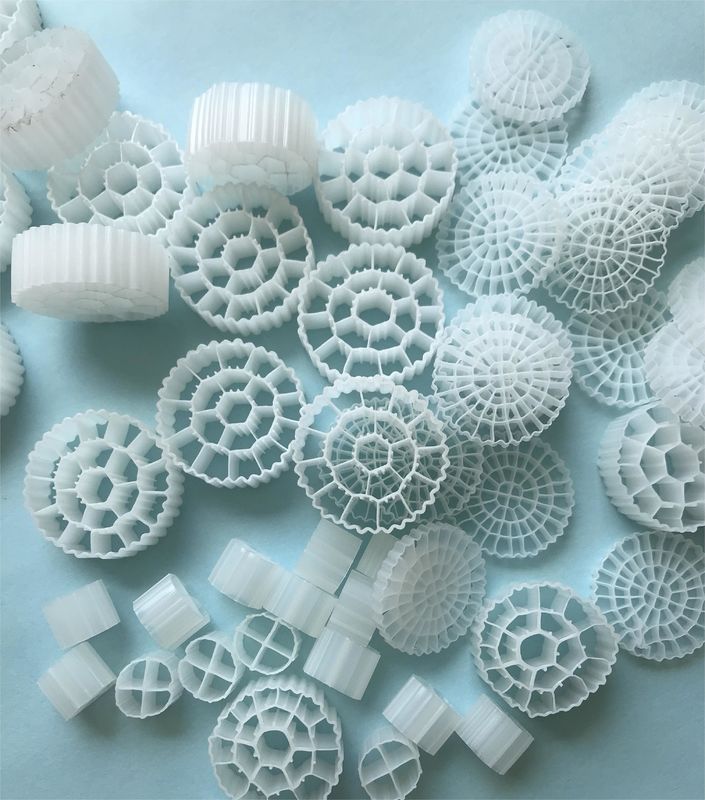
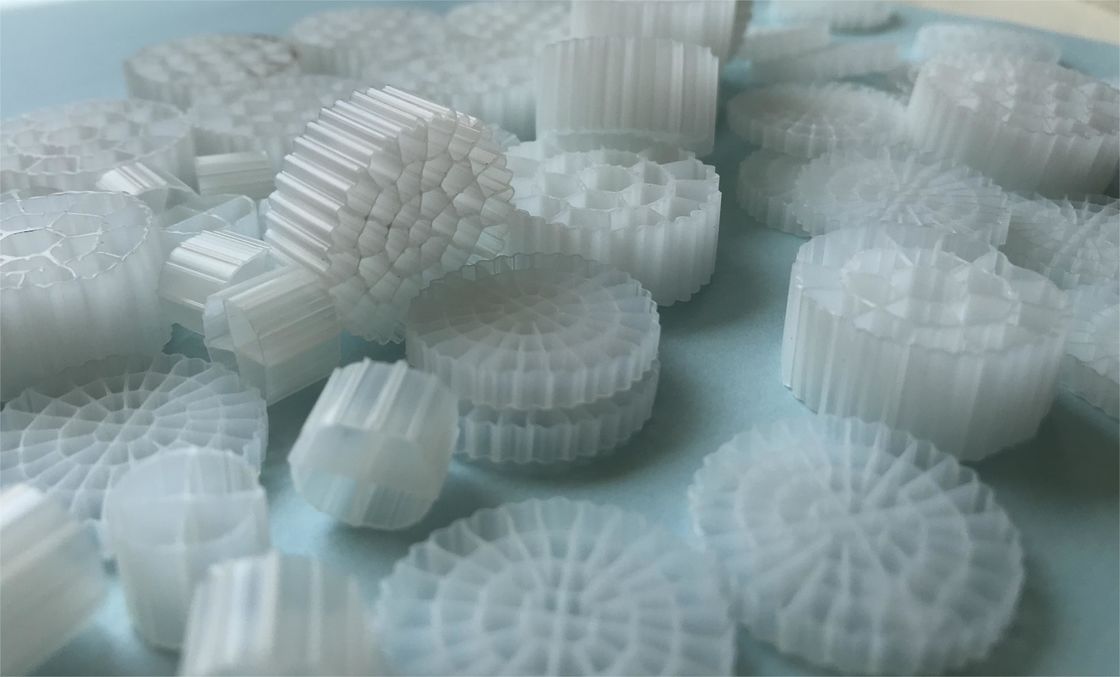
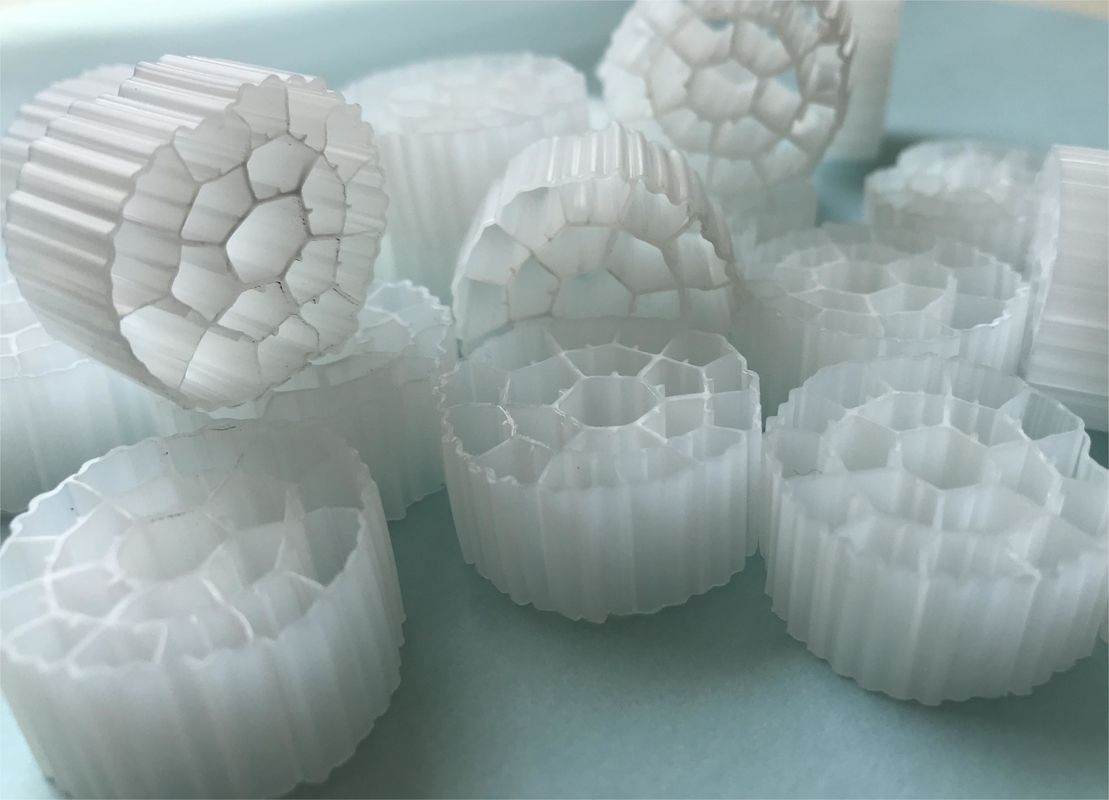
The MBBR system consists of an aeration tank (similar to an activated sludge tank) with special plastic carriers that provide a surface where a biofilm can grow. There is a wide variety of plastic carriers used in these systems. These carriers vary in surface area and in shape, each offering different advantages and disadvantages.
The surface area plays a very important role in biofilm formation. Free-floating carriers allow biofilms to form on the surface, therefore a large internal surface area is crucial for contact with water, air, bacteria, and nutrients. The carriers will be mixed in the tank by the aeration system and thus will have good contact between the substrate in the influent wastewater and the biomass on the carriers
The most preferable material is currently high-density polyethylene (HDPE) due to its plasticity, density, and durability.
To achieve a higher concentration of biomass in the bioreactors, hybrid MBBR systems have been used where suspended and attached biomass co-exist contributing both to biological processes.

FEATURES
-
Large specific surface area, more attached microorganisms
-
No need bracket, easy to fluidize, save energy
-
Fast and easily to hang membrane, high biological activity
-
Strong impact resistance, long lifetime
-
Excellent nitrogen and phosphorus removal effect
-
Small footprint, simple and flexible operation management
-
Good hydrophilicity, good treatment effect
-
Relying on biofilm treatment, reduces the remaining sludge

CURRENT USAGE
Today, MBBR technology is used for municipal sewage treatment, industrial wastewater treatment, and decentralized wastewater treatment. This technology has been used in many different industries, some of them being:
- Automotive industry
- Chemical industry
- Food and beverage
- Metal plating and finishing
The MBBR system is considered a biofilm or biological process, not a chemical or mechanical process. Other conventional biofilm processes for wastewater treatment are called trickling filters, rotating biological contactors (RBC), and biological aerated filters (BAF).

APPLICATION


ADVANTAGES
Biofilm processes in general require less space than activated sludge systems because the biomass is more concentrated, and the efficiency of the system is less dependent on the final sludge separation.MBBR systems do not need recycling of the sludge, which is the case with activated sludge systems.
The MBBR system is often installed as a retrofit of existing activated sludge tanks to increase the capacity of the existing system. The degree of filling of carriers can be adapted to the specific situation and the desired capacity. Thus an existing treatment plant can increase its capacity without increasing the footprint by constructing new tanks.
Some other advantages are:
- Increased performance and volumetric treatment capacity
-
Higher effective sludge retention time (SRT) which is favorable for nitrification
-
Responds to load fluctuations without operator intervention
-
Lower sludge production
-
Less area required
-
Resilient to toxic shock
-
Process performance independent of secondary clarifier (due to the fact that there is no sludge return line).

SPECIFICATON


Q: Do you have any MOQ limit?
A: Greater than 1 (not free shipping)
Q: Can you print our logo on the outer package?
A: Yes.
Q: Can we visit your company and factory?
A: Yes, you can.
Q: Can you accept mixed batches of different products?
A: Yes.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 




